Connect Public, Private and Organization GitHub Repositories to ArgoCD
ArgoCD is a popular GitOps tool that automates deployment and provides a streamlined continuous delivery experience. To deploy applications using ArgoCD, it needs to be connected to the repository where the application code is stored. There are four ways to connect private repositories to ArgoCD:
via HTTPS
via SSH
via GitHub App
via Google Connect
Here we are exploring two ways :

via HTTPS
Using UI
Using CLI
via SSH
Using UI
Using CLI
1) via HTTPS:
repoURL: https://
a) Private Repository in personal account
Username: <github-username>
Password: <github-password>
b) Private repo in organization and your account has organization access. username: <any non-empty string>
password: <personal-access-token>
A) Using UI
Open ArgoCD UI and navigate to the Settings --> Repositories tab.
Click on the CONNECT REPO USING HTTPS button.
Enter the repository URL in the REPO URL field.
If the repository is a private repository in your personal account, enter your GitHub username and password in the
USERNAMEandPASSWORDfields.If the repository is a private repository in an organization and your account has organization access, enter a
personal access token (PAT)in thePASSWORDfield.
How to create Personal Access Token:
create a PAT:
Go to your GitHub profile settings and select
Developer Settings.Click on
Personal access tokens.Click on
Tokens(classic).Click on
Generate New Token.Enter a name for the token and select the required scopes.
Click on
Generate token.Copy the token value (this is the value of your password field).
Note: If SSO is enabled for the organization, make sure to click on configure SSO button and authorize the respective organization.
B) Using CLI
Open a terminal and run the following command, replacing the placeholders with your values:
argocd repo add <repo-url> --username <github-username/non-empty string> --password <github-password/PAT>
2) via SSH
repoURL: git@
Create SSH Keys
create ssh key using the below command
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C <email>
This command creates two keys private key(id_rsa) and public key(id_rsa.pub) - Asymmetric Key Encryption
View ssh key
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
Add public key to GitHub
- Copy your public SSH key to your clipboard. You can do this by running the following command in your terminal:
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
This will output your public SSH key, which you can then copy to your clipboard.
Go to your GitHub profile and click on "Settings" in the top-right corner.
Click on "SSH and GPG keys" in the left-hand menu.
Click on the "New SSH Key" button.
Give your key a descriptive title in the "Title" field (e.g., "My Work Laptop").
Paste your public SSH key content into the "Key" field.
Click on the "Add SSH key" button.
If you are a member of an organization that has enabled SSO (Single Sign-On), you will need to click on the "Configure SSO" button and authorize your respective organization. This will allow you to access the organization's repositories using your SSH key.
Your SSH key is now added to your GitHub account and you can use it to access repositories that you have been granted access to.
A) using UI
Go to Repositories and provide ssh private key which is located at cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa
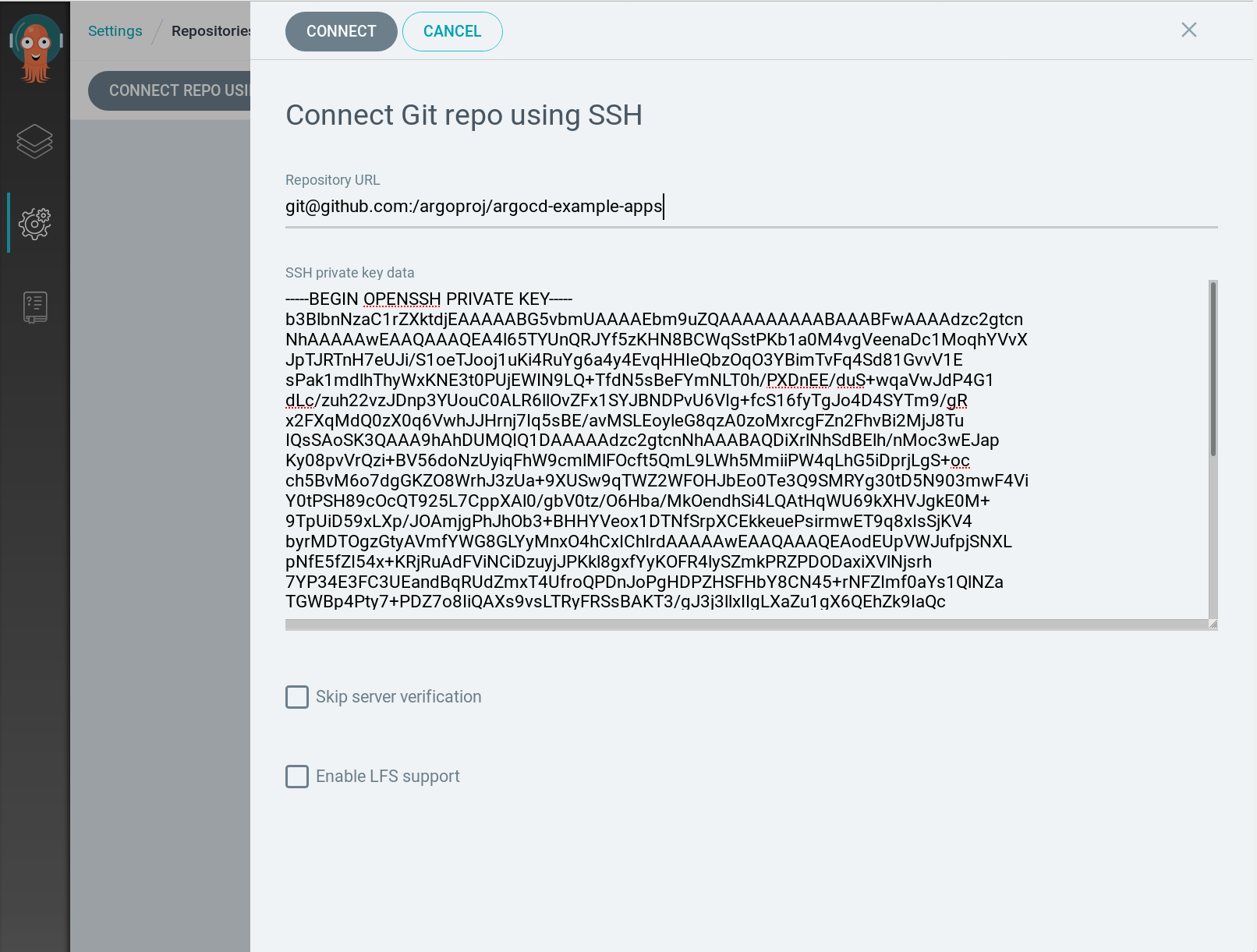
B) using CLI
argocd repo add <repo-url> --ssh-private-key <private-key-path>
argocd repo add git@github.com:argoproj/my-private-repository --insecure-ignore-host-key --ssh-private-key-path ~/.ssh/id_rsa
Declarative Approach using Kubernetes secret
Github Repo Using HTTPS:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: private-repo
namespace: argocd
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
stringData:
type: git
url: <https://github.com/argoproj/private-repo>
password: <my-password/personal-access-token>
username: <my-username/non-empty-string>
To skip certificate validation add insecure: true
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: private-repo
namespace: argocd
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
stringData:
type: git
url: <https://github.com/argoproj/private-repo>
password: <my-password/personal-access-token>
username: <my-username/non-empty-string>
insecure: true
Using SSH:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: private-repo
namespace: argocd
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
stringData:
type: git
url: <git@github.com:argoproj/my-private-repository>
sshPrivateKey: |
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
